
- #Start azure storage emulator install
- #Start azure storage emulator software
- #Start azure storage emulator code
Call the GetListImages() method to fetch all the uploaded file URLs.Call the Index() method to upload the file get the URL of the uploaded file.
#Start azure storage emulator code
So, now our code is ready to perform Upload and Fetch files operation from the Azure local Storage Emulator.

Var response = await container.ListBlobsSegmentedAsync("", true, BlobListingDetails.None, 500, null, null, null) Get all the uploaded file URLs from Azure storage Var fileURL = await GetReadUrlAsync(responseGuid) Var responseGuid = await UploadFromFileAsync("D://Download.jpg", "image/png") //Give the File here with File Type Upload file and get URL of the file from Azure storage

Using (var fileStream = System.IO.File.OpenRead(filePath))Īwait blockBlob.UploadFromStreamAsync(fileStream) String sasBlobToken = blob.GetSharedAccessSignature(sasConstraints) Īsync public Task UploadFromFileAsync(string filePath, string contentType)ĬloudBlockBlob blockBlob = container.GetBlockBlobReference(guid) ī = contentType SasConstraints.SharedAccessExpiryTime = () SasConstraints.SharedAccessExpiryTime = (hours) SasConstraints.SharedAccessStartTime = (-5) SasConstraints.Permissions = SharedAccessBlobPermissions.Read SharedAccessBlobPolicy sasConstraints = new SharedAccessBlobPolicy() _container = client.GetContainerReference(containerName) Īsync public Task GetReadUrlAsync(string blobId, int hours = 0)ĬloudBlobContainer container = await GetContainerAsync() ĬloudBlockBlob blob = container.GetBlockBlobReference(blobId) If (_container != null) return _container ĬloudBlobClient client = StorageAccount.CreateCloudBlobClient() It is now replaced by Azurite, the open source successor that is based on Node.js.
#Start azure storage emulator software
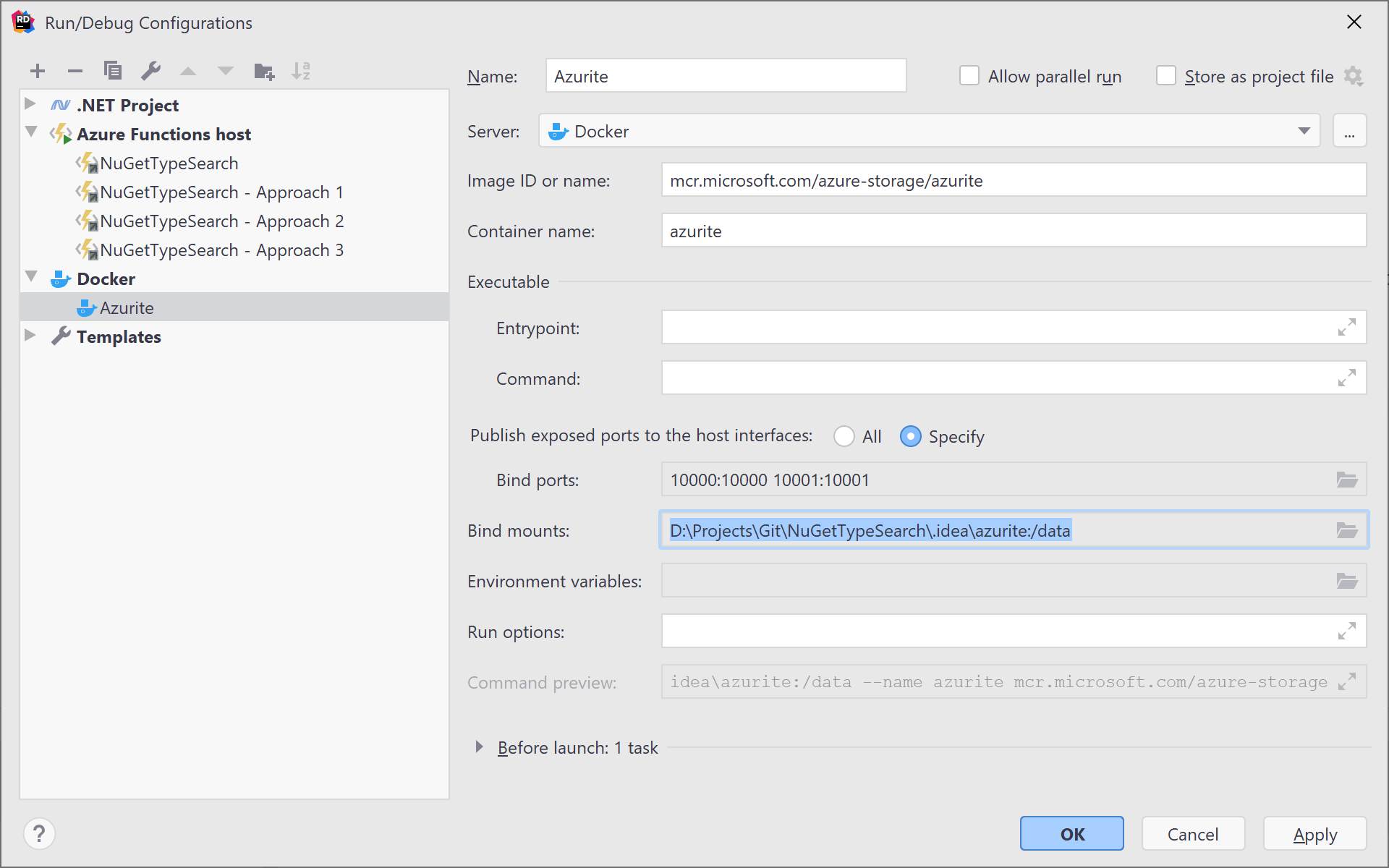
In early stages, Microsoft Azure Storage Emulator is a software that runs on Windows machine to emulate Azure storage services for local development and testing. Private CloudStorageAccount StorageAccount Use Azurite (Microsoft Azure Storage Emulator) for Development and Testing. Private CloudStorageAccount _storageAccount Private readonly string containerName = "mycontainer" Private readonly string connectionString = "UseDevelopmentStorage=true" Step-2: Add HomeController.cs in Controllers folder : using Step-1: In the NuGet Package Manager, search for and select WindowsAzure.Storage. Note: Remember you have to run this emulator before you run the project.
#Start azure storage emulator install
You can download the Azure Storage Emulator here and Install it on your pc.

When you’re happy with how your application is working in the emulator, switch to using an Azure subscription account in the cloud. You can test your app against the storage services locally without creating an Azure subscription account or incurring any costs. Testing against the local storage will save some storage costs.The Microsoft Azure Storage Emulator provides functionality to emulates the Azure Blob, Queue, and Table services for local development purposes. Testing an Azure application will have multiple phases, but initially (I spent quite a bit of time trying to tweak AzureĬonfig files to get an application to use the Storage Emulator before Testing your application.) The SDK has all the plumbing for utilizing Have to start the Compute Emulator and Development Storage before $queueClient = new Microsoft_WindowsAzure_Storage_Queue() Īssuming you have installed all the prerequisites for using the Windows Azure SDK for PHP, that’s it. $blobClient = new Microsoft_WindowsAzure_Storage_Blob() $tableClient = new Microsoft_WindowsAzure_Storage_Table() When constructing a new table, blob, or queue client, simply omit the constructor parameters: This example runs the service in the Azure emulator and launches a new browser window on the emulated service. Examples Example 1: Start the emulator and launch a browser PS C:> Start-AzureEmulator -L. Turns out, the answer is very simple, although somewhat difficult to The Start-AzureEmulator cmdlet starts both the compute and storage emulators and hosts the current service in the compute emulator. This is a short post to address this question: How do I use the local Storage Emulator (formerly known as Development Storage) when using the Windows Azure SDK for PHP? The Windows Azure Command Line Tools for PHP provide an option for running an application locally in the Compute Emulator,īut I didn’t see an option for using the local Storage Emulator.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
